Organizations usually choose local LLM + RAG for very practical reasons:
- Sensitive data cannot leave the network
- Cloud inference costs are becoming unpredictable
- AI is used frequently and must be always available
- The goal is a daily productivity tool, not a demo
Very quickly, teams discover a hard truth:
The success of local LLM + RAG depends far more on architecture and practices than on the model itself.
This article summarizes field-tested best practices to help you avoid costly mistakes.
One-Sentence Takeaway
A successful local LLM + RAG system is not about “running a model,”
but about designing inference, memory, data flow, and operations as a complete system.
A Critical Premise: Local LLM + RAG Is an Inference System
First, internalize this:
Local LLM + RAG is a long-running inference service.
It is not:
- A training cluster
- A batch job
- A one-off experiment
👉 Your mindset should resemble enterprise service design, not research prototyping.
Best Practice 1: Choose Stability Over Maximum Model Size

Practical guidance
- Prefer 7B–8B class models
- Choose models with large communities and mature tooling
- Do not chase the largest parameter count
📌 Why?
- RAG provides knowledge
- The model handles understanding and generation
- Stability and predictability beat raw capability
Best Practice 2: Always Budget VRAM Headroom
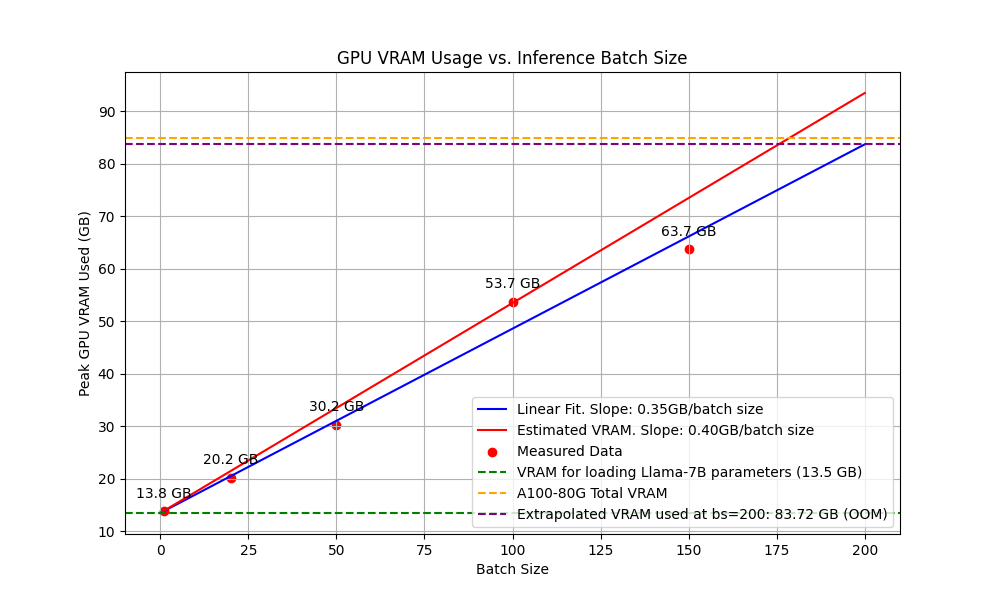
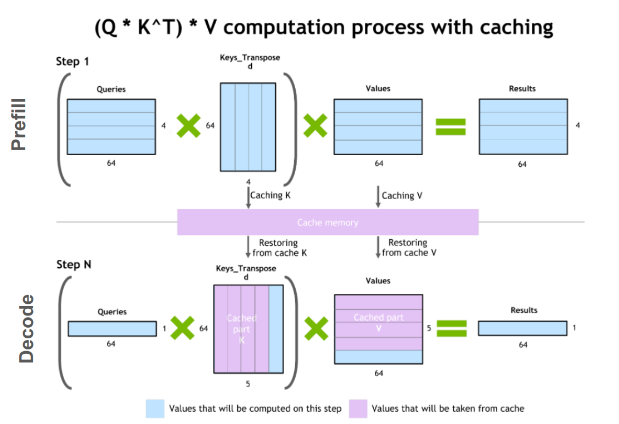
Remember this rule:
Model size ≠ real VRAM usage
VRAM is also consumed by:
- KV cache
- Context length
- Runtime and framework buffers
Field experience
- 16 GB for a 7B model is barely sufficient
- 24 GB is where inference becomes comfortable
👉 No VRAM headroom = unstable system.
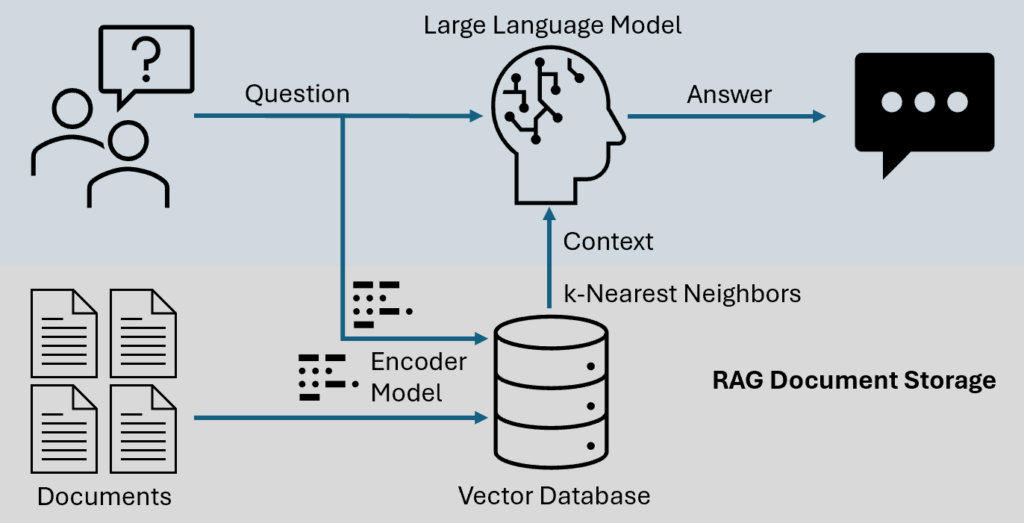
Best Practice 3: Keep RAG Strictly in the Inference Layer
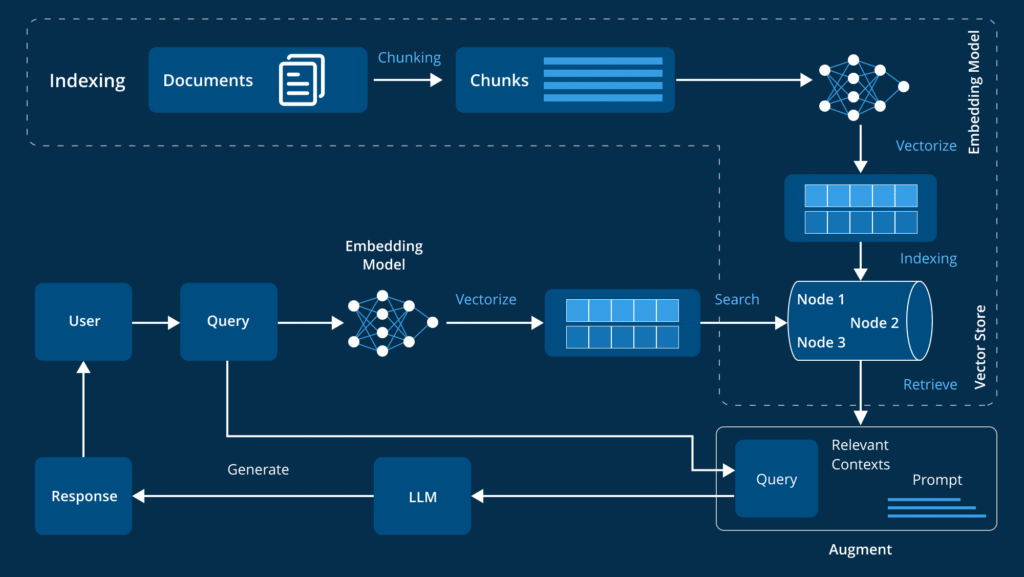

Correct approach
- Document embedding: offline
- Retrieval, ranking, context assembly: at inference time
- No knowledge fine-tuning
📌 This allows:
- Instant document updates
- Immediate removal of outdated data
- No retraining cycles
👉 RAG exists to avoid retraining—not replace it.
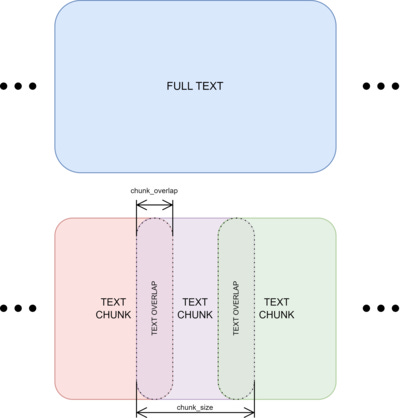
Best Practice 4: Document Chunking Matters More Than You Think
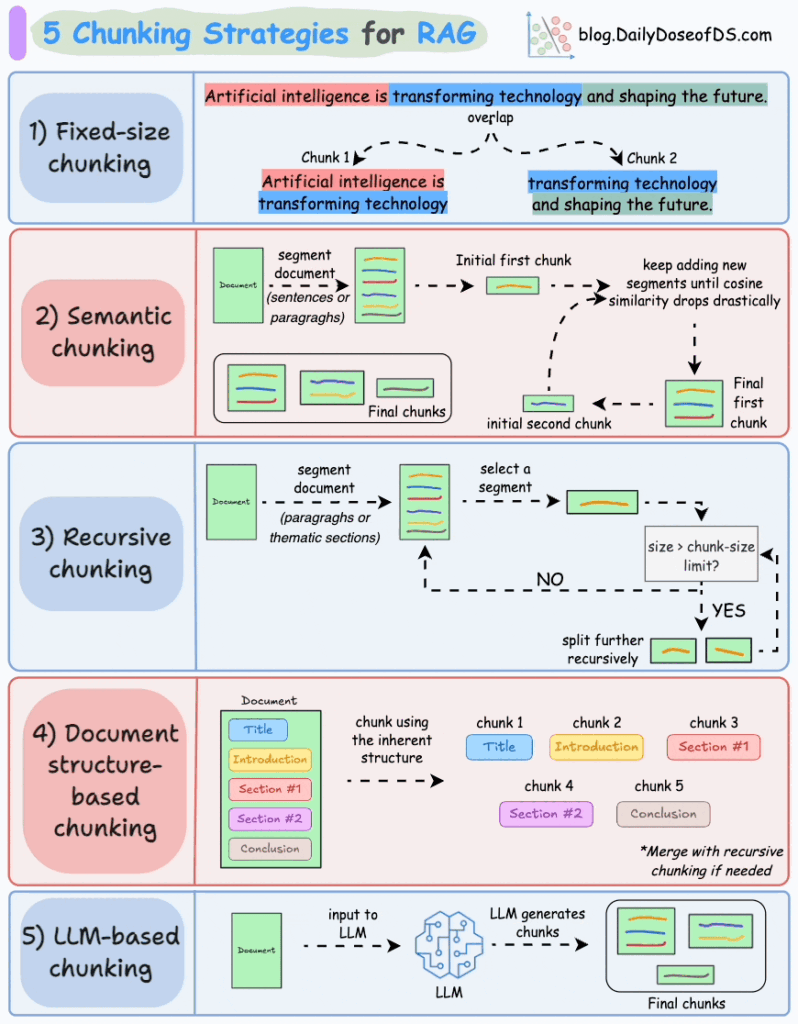
Common mistakes
❌ Indexing entire documents
❌ Chunks that are too large (poor recall)
❌ Chunks that are too small (loss of meaning)
Recommended approach
- 300–800 tokens per chunk
- 10–20% overlap
- Preserve headings and section metadata
👉 Chunking defines the upper bound of RAG quality.
Best Practice 5: Context Length Must Be Actively Controlled
Core principles
- Never inject everything retrieved
- Enforce Top-K limits
- Cap total token count
Practical techniques
- Question-aware retrieval
- Summarize before injection
- Summarize or truncate conversation history
👉 Context is your most expensive resource.
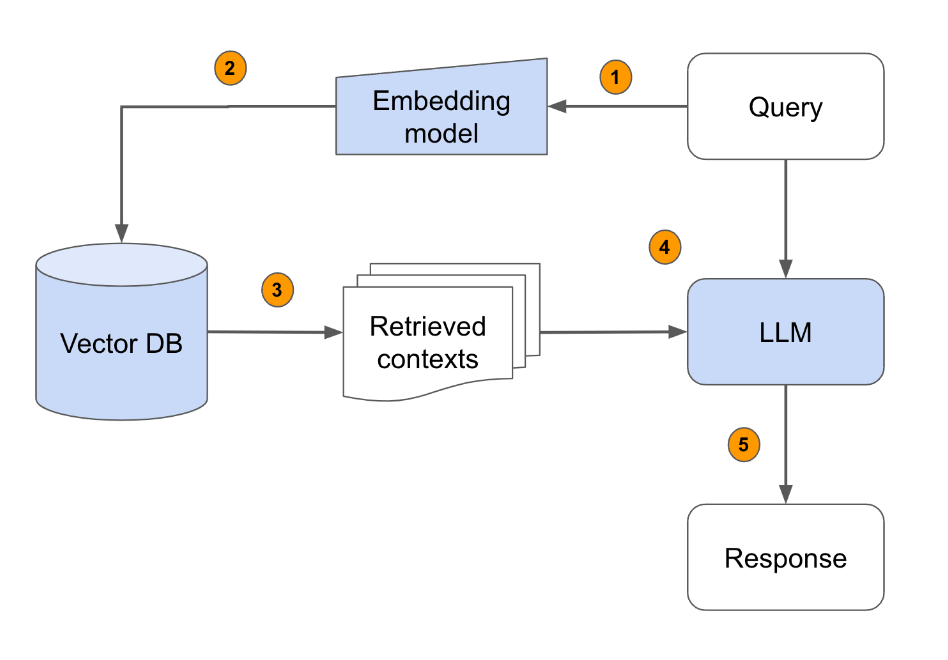
Best Practice 6: RAG Is More Than Vector Search
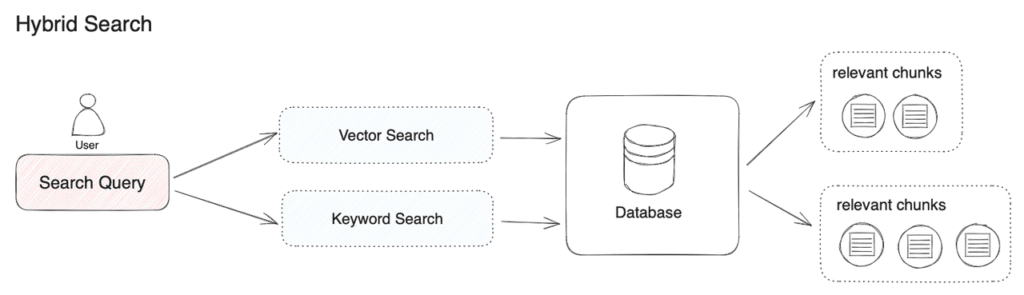
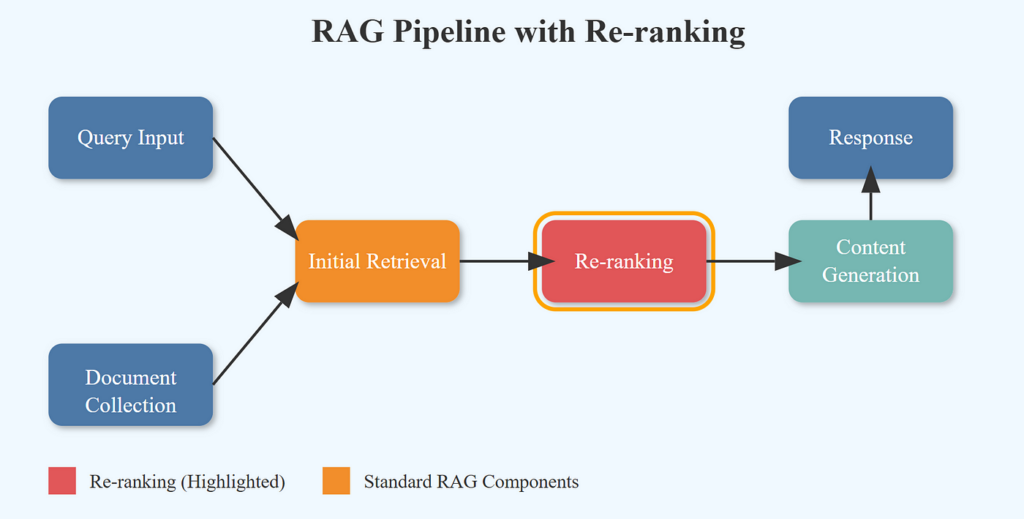
Mature RAG systems often combine:
- Keyword search (BM25)
- Vector similarity search
- Rerankers (cross-encoders)
📌 This dramatically reduces:
- Irrelevant retrieval
- Hallucinations
Best Practice 7: Build Inference-Layer Safeguards
Essential protections
- Maximum concurrency limits
- Request queues
- OOM protection
- Timeouts
📌 If a local LLM crashes, everyone goes down together.
Best Practice 8: Monitoring Beats Micro-Optimization
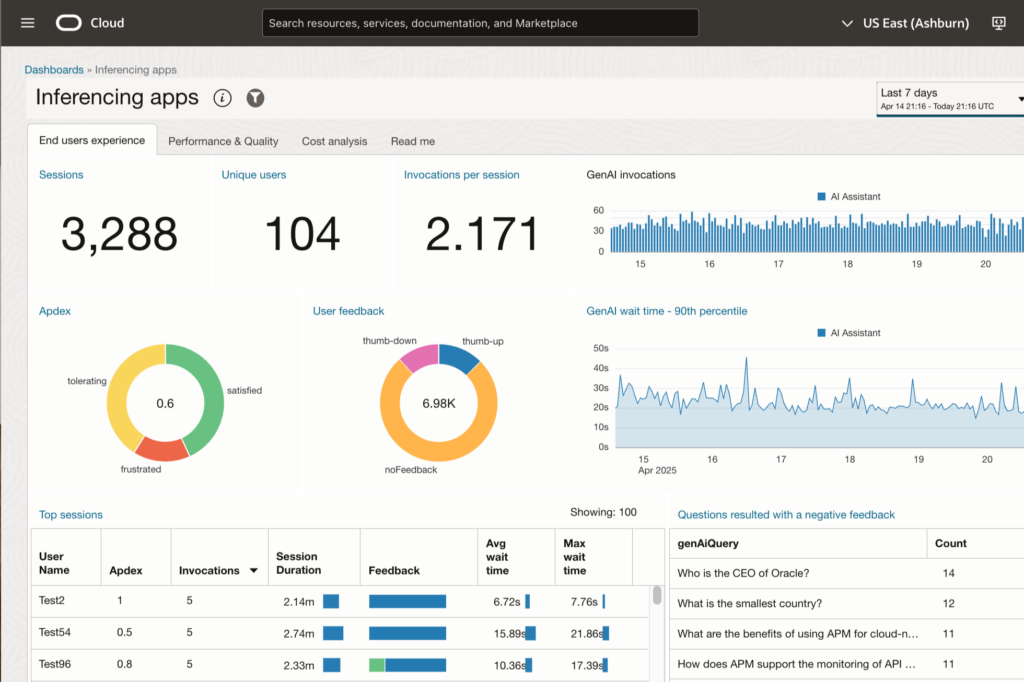
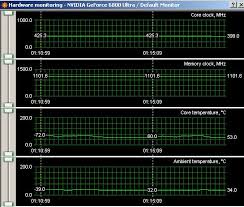
At a minimum, monitor:
- VRAM usage
- Context token count
- Latency (P95/P99)
- Error rates
👉 An unmonitored AI system will fail at the worst possible moment.
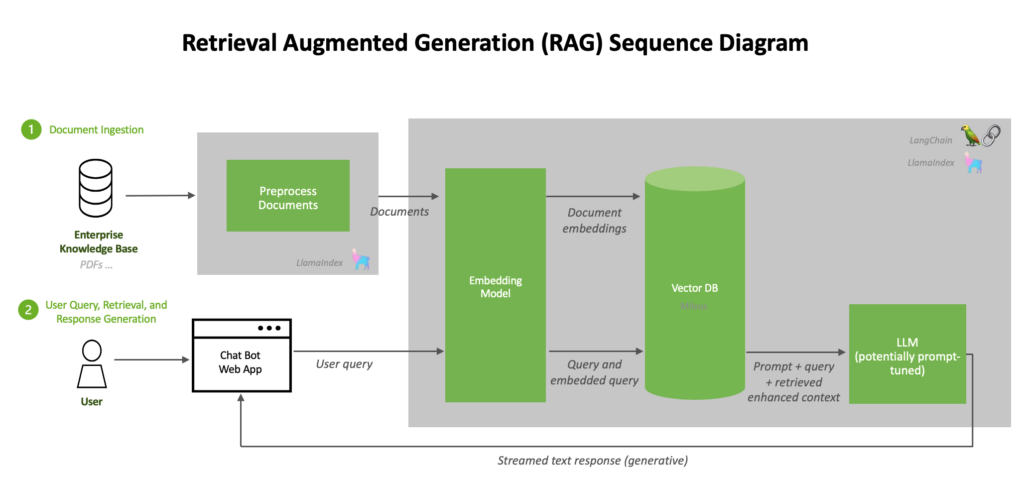
A Maintainable Local LLM + RAG Architecture


Recommended layering
- API / Gateway
- Inference Service (LLM)
- RAG Service
- Vector Database
- Document Ingestion Pipeline
- Monitoring & Logging
👉 Clear boundaries are the foundation of long-term operability.
One Sentence to Remember
The success of local LLM + RAG depends not on model size,
but on having clear boundaries and controls at every layer.
Final Conclusion
Local LLM + RAG is a systems engineering problem, not a model deployment task.
If you:
- Manage VRAM carefully
- Control context growth
- Keep RAG in the inference layer
- Add basic monitoring and safeguards
👉 You will end up with a stable, controllable, and cost-efficient AI platform.